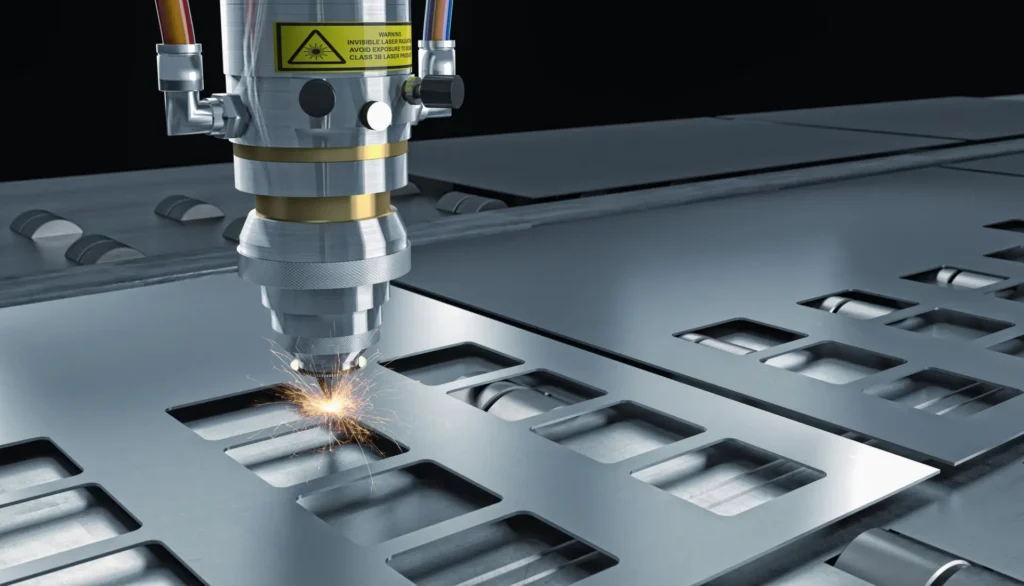
Laser cutting technology has been used to achieve precise cuts in sheet metal fabrication with the aid of CNC machines. The process is widely employed for making metal parts due to its high repeatability and advanced solutions. In this article, Firstpart explains laser cutting technology and the numerous benefits for sheet metal fabrication.
What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is one of the precision sheet metal services offered at Firstpart. It is a high-accuracy, top-precision CNC process that uses a high-power laser beam directed at a sheet metal to cut through the sheet metal. Laser cutting can be used with metals, wood, and polymers but mainly for sheet metal fabrication, where there is no custom-designed tool to make complex metal parts.
Laser cutting is well suited for low-volume production and small-batch or one-off runs. The key advantages are precision, repeatability, and excellent surface finish. Laser cutting is used with metals no more than 10mm in thickness (sheets) and is particularly favored in medical manufacturing for its accuracy and consistency.
Laser Cutting Operations
The laser cutting operation can be summarized in 5 simple steps. Here is an overview of how sheet metals are processed once the part has been placed onto the bed:
1. The laser beam power is set to match the properties of the material to be cut and the sheet metal thickness.
2. The CAD file is loaded into a series of commands that will direct the laser beam controlled by the CNC or laser cutting machine.
3. The sheet metal is cut to fit the machine’s bed workpiece and secured to the machine bed with a clamp.
4. The workpiece is then cut by the laser beam, which focuses from section to section till the final form is attained.
5. Sheet metal parts that have been cut may then be further processed or finished to meet client specifications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Cutting
The major advantages of laser cutting are around its versatility, precision, and speed. Laser cutting has an almost unmatched range of sheet metals that it can cut, engrave or process. Regardless of complexity and size, laser cutting can achieve exact cuts and markings for materials within the 10mm to 100mm thickness. It is also significantly faster and more efficient than conventional cutting, shearing, and manual processing sheet metals.
The main downside of laser cutting is the limitation in the thickness of materials that can be cut. While this varies from laser to laser and the equipment’s power, laser cutting will usually struggle with materials above 100mm. Because of the nature of the process, there are also potentially higher costs to accommodate the increased power and energy consumed during operation.
Type of Laser Cutters
There are three main types of methods for laser cutting. These methods vary in their capabilities, states, and performance.
I. CO2 gas
CO2 gas laser cutters are gas-powered solutions that compose of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium. They are electrically stimulated and emitted at around 10.6mm of wavelength. CO2 lasers are the most widely used laser types. The advantages of this type of laser cutters lie in their high efficiency, low-cost and widespread availability.
II. Crystal laser cutters
Both ND:YVO and ND:YAG lasers fall under the categories of solid-state laser cutters. These laser cutters can cut through materials with higher strength and thickness than those handled with CO2 cutters. They have a shorter wavelength (1.064mm) and higher intensity, which equals shorter processing time, increased energy consumption, higher cost, improved reliability, and performance.
Crystal laser cutters wear quicker than CO2 cutters due to their high concentration and intensity. They are particularly used for boring and engraving operations and are the most expensive laser cutters.
III. Fiber laser cutters
Fiber lasers also belong to the class of solid-state lasers. They operate at an energy-efficiency triple that of CO2-based cutters. Fibre laser cutters use fiberglass with no moving parts to intensify the output of base seed lasers. They are easier to maintain and can run at faster speeds when cutting sheet metals. Fiber lasers are widely used for metal engraving, cutting reflective materials, and high-contrast plastic markings without consequence. They can handle up to 100 times the intensities of CO2 lasers at the same power consumption level.
These fiber laser cutters’ benefits include higher productivity, increased reliability, shorter processing times, and minimal maintenance as there are no moving parts.
How much does Laser Cutting cost?
It is difficult to determine the cost of a laser cutting operation without having details of the project. The primary criteria affecting the price of laser cutting are material type, material thickness, project design, and the type of laser to be used. To receive an accurate quote for your project, upload your CAD file to Firstpart for a free and instant quote.
Laser Cutting Metals
The versatility of laser cutting means that it can be cut through plastic, ceramics, wood, paper, and metals. For sheet metals, the most common metals processed with laser cutting systems include Aluminum, Silver Copper, and Stainless Steel, and Titanium alloys.
Contact us for your Sheet Metal Services today
FirstPart’s expertise and experience in sheet metal services provides customers with a one-stop-shop service on all sheet metal projects. From design to fabrication, finishing and post-fabrication, our latest technologies, engineering workforce and machine investments all ensure that we stay ahead of our competition to provide high quality parts at the most competitive prices. Contact us today for sheet metal services and take a look at all of our sheet metal capabilities including pressing, forming, CNC cutting and laser cutting.